Understanding WebSockets and Their Use in FastAPI
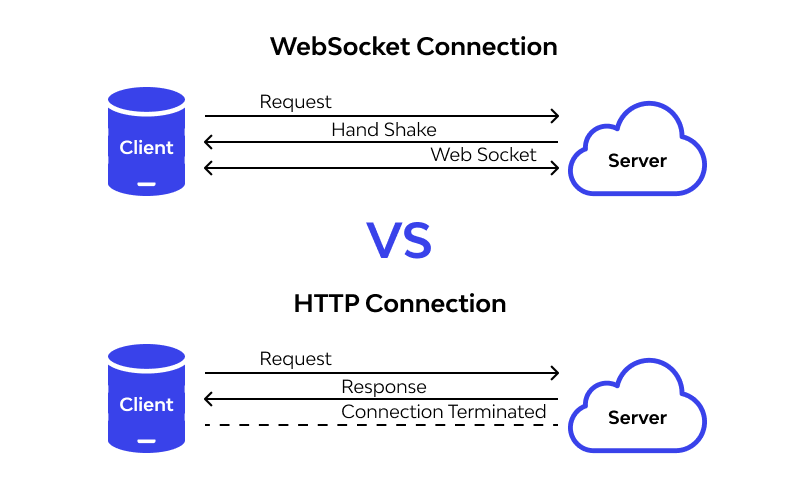
In modern web applications, real-time communication has become a necessity. Traditional HTTP works on a request-response model: the client sends a request, and the server responds. However, this model is inefficient for scenarios where updates need to be pushed to the client instantly, such as chat applications, online games, live dashboards, or collaborative tools. This is where WebSockets come into play.
Why WebSockets Exist
WebSockets provide a persistent, bidirectional communication channel between client and server over a single TCP connection. Unlike HTTP, which is stateless and requires repeated requests to fetch updates, WebSockets keep the connection open, allowing both parties to send messages at any time. This reduces latency, minimizes overhead, and makes real-time interactions much more efficient.
Key Benefits of WebSockets:
- Persistent connection: no need to re-establish communication on every interaction.
- Real-time updates: servers can push data instantly to clients.
- Lower overhead: reduces the constant polling required in traditional HTTP.
- Bidirectional: both client and server can send and receive messages at any time.
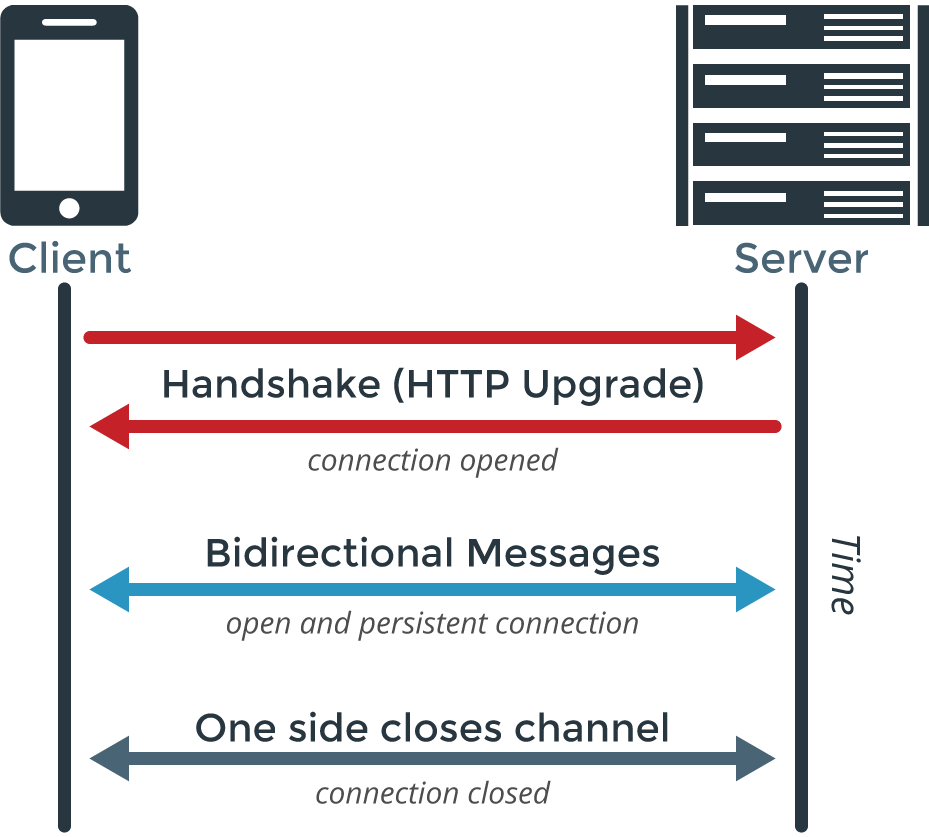
Example: WebSocket in FastAPI
FastAPI makes working with WebSockets straightforward. Below is a simple example of a chat-like connection where clients can send and receive messages in real time:
from fastapi import FastAPI, WebSocket
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
app = FastAPI()
html = """
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>WebSocket Chat</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>FastAPI WebSocket Example</h1>
<textarea id="messages" rows="10" cols="30"></textarea><br>
<input id="messageInput" type="text">
<button onclick="sendMessage()">Send</button>
<script>
var ws = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8000/ws");
ws.onmessage = function(event) {
var messages = document.getElementById("messages");
messages.value += event.data + "\\n";
};
function sendMessage() {
var input = document.getElementById("messageInput");
ws.send(input.value);
input.value = "";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
"""
@app.get("/")
async def get():
return HTMLResponse(html)
@app.websocket("/ws")
async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket):
await websocket.accept()
while True:
data = await websocket.receive_text()
await websocket.send_text(f"Message received: {data}")
When to Use WebSockets
WebSockets are particularly useful in applications that require constant updates without refreshing the page. Some examples include:
- Chat and messaging platforms
- Live notifications (stock prices, sports scores, social media updates)
- Online multiplayer games
- Collaborative tools (document editing, whiteboards)
- Real-time analytics dashboards
Conclusion
WebSockets solve the limitations of the request-response model of HTTP by enabling persistent, bidirectional communication. With frameworks like FastAPI, implementing WebSockets is seamless, making it easier than ever to build modern applications that require real-time interactivity and low latency.